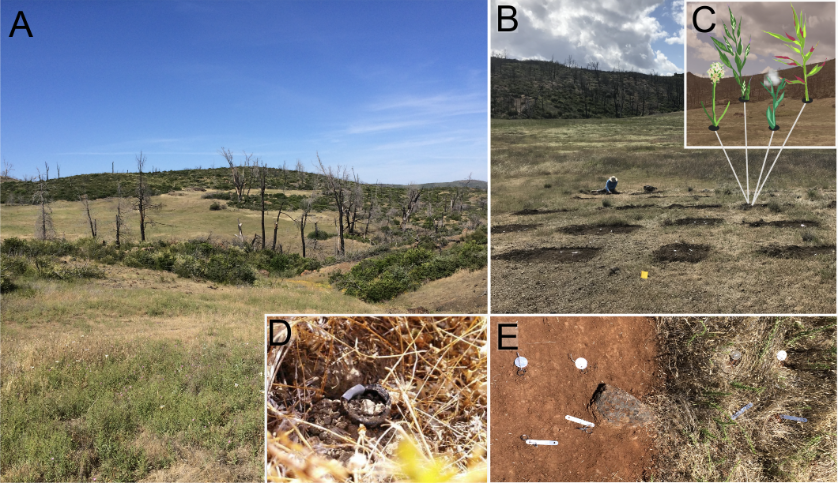
F I G U R E 1. McLaughlin Natural Reserve in Northern California, USA. (A) Image of one of the six sites used in the experiment. (B) Image of a grid. There were three grids per site. (C) Cartoons of focal species, from left to right: Plantago erecta, Bromus hordeaceus, Micropus californicus, and Festuca microstachys. (D) Image of polypipe used to sow seeds. (E) Image of a block, with the left plot cleared of biotic materials (without neighbors) and the right plot with biotic materials intact (with neighbors). There were 25 blocks per grid. Photo credits: (A, E) by Megan Szojka; (B, D) by Rachel Germain. Digital art in (C) was created by Megan Szojka.
Abstract
For decades, community ecologists have examined how diversity varies with ecosystem productivity. Despite this long history, tests of hypothesized mechanisms, namely the interplay between environmental filtering, biotic interactions, and dispersal, are lacking, largely due to the intractability of using traditional approaches. Across a productivity gradient in a serpentine grassland (California,USA), for four annual plant species, we coupled local productivity estimates, occupancy surveys, and measures of persistence tested on transplants under natural conditions and when interactions with neighbors were experimentally reduced. We found a positive effect of productivity on diversity (i.e., the proportion of our focal species occupying a location) despite strong competition limiting species persistence in productive environments. Additionally, across species and for the community, we found a strong mismatch between species occupancy versus persistence, largely due to dispersal excess causing sink populations with negative growth rates. Our results suggest that diversity–productivity relationships can be largely driven by dispersal and its interactive effects with local biotic and abiotic conditions.