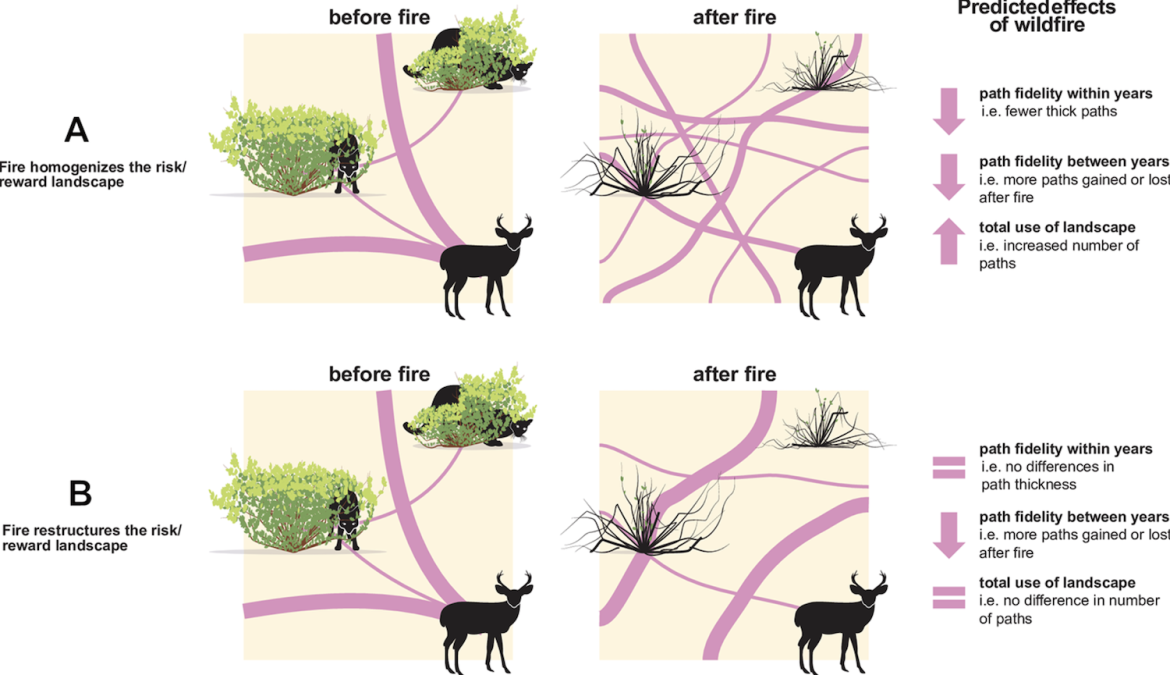
Fig 1. Predicted effects of wildfire on deer movement in support of alternative hypotheses. Effects include a change in the path fidelity within years (i.e., their thickness, a proxy for the directedness of movement), changes in path fidelity between years (i.e., the persistence of paths between years), and overall activity (i.e., total number of paths, with or without weighting by path thickness). All predictions are relative to sites with no recent history of fire to control for temporal changes in landscape use by deer unrelated to wildfire (a feature of Before/After Control/Impact (’BACI’) experimental designs). If wildfire has no effect on the spatial structure of risks and rewards, then we would expect no difference before vs after the fire. Equal sign = no difference between burned and unburned. Artwork is original and created by S. Heredia (https://www.sylviaheredia.com/).
Abstract
Animals navigate landscapes based on perceived risks vs. rewards, as inferred from features of the landscape. In the wild, knowing how strongly animal movement is directed by landscape features is difficult to ascertain but widespread disturbances such as wildfires can serve as natural experiments. We tested the hypothesis that wildfires homogenize the risk/reward landscape, causing movement to become less directed, given that fires reduce landscape complexity as habitat structures (e.g., tree cover, dense brush) are burned. We used satellite imagery of a research reserve in Northern California to count and categorize paths made primarily by mule deer (Odocoileus hemionus) in grasslands. Specifically, we compared pre-wildfire (August 2014) and post-wildfire (September 2018) image history layers among locations that were or were not impacted by wildfire (i.e., a Before/After Control/Impact design). Wildfire significantly altered spatial patterns of deer movement: more new paths were gained and more old paths were lost in areas of the reserve that were impacted by wildfire; movement patterns became less directed in response to fire, suggesting that the risk/reward landscape became more homogenous, as hypothesized. We found evidence to suggest that wildfire affects deer populations at spatial scales beyond their scale of direct impact and raises the interesting possibility that deer perceive risks and rewards at different spatial scales. In conclusion, our study provides an example of how animals integrate spatial information from the environment to make movement decisions, setting the stage for future work on the broader ecological implications for populations, communities, and ecosystems, an emerging interest in ecology.